

Iron oxide + carbon → iron + carbon dioxide
#Reactivity series chemistry gcse pdf#
Cambridge IGCSE GCSE Chemistry PDF notes includes high school question papers. If the metal being extracted is lower than carbon in the series, such as iron, the carbon will displace it and the result will be From quite simple experiments, metals can be arranged in order of their reactivity in what we call a reactivity series. species, reactive intermediates and molecules which will perhaps never be. This reaction is irreversible, as copper isn’t reactive enough to be able to displace the magnesium.Ĭarbon is included in the series because carbon is used in the extraction of several metals from their ores (ores are usually metal oxides). Unit C2: Further Chemical Reactions, Rates and Equilibrium, Calculations and Organic Chemistry. Understanding the reactivity series is fundamental to chemistry it explains why most reactions happen and what changes the particles will undergo during the reaction. of metals is a chart showing metals in order of decreasing reactivity. Copper is less reactive than magnesium, and so it has been displaced by magnesium to form magnesium oxide and copper. 2.1.1 recall the reactivity series of metals, including K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe and Cu 2.1.4 explain and describe the displacement reactions of metals with other metal ions in solution CCEA Double award science. The reactivity series lists elements (mostly metals) in order of decreasing reactivity. All metals higher in the series will displace a metal lower than it from a compound. Displacement means that one of the elements has been pushed out of the compound it was in and replaced by a more reactive element (hence, displaced). Test your knowlege on reactions with metals, acids, alkalis and salts, titrations.Magnesium + copper(II) oxide → magnesium oxide + copper It is a watered-down version of the Electrochemical Series. Plants absorb mineral ions through their roots. The reactivity series of metals shows how reactive some elements are compared with others. The circus of activities is used to pupils can work at their own pace developing their independence. 0620 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Specimen Papers. Methods of extraction are not included because I have given them a whole separate lesson. Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry past and specimen paper questions and answers.
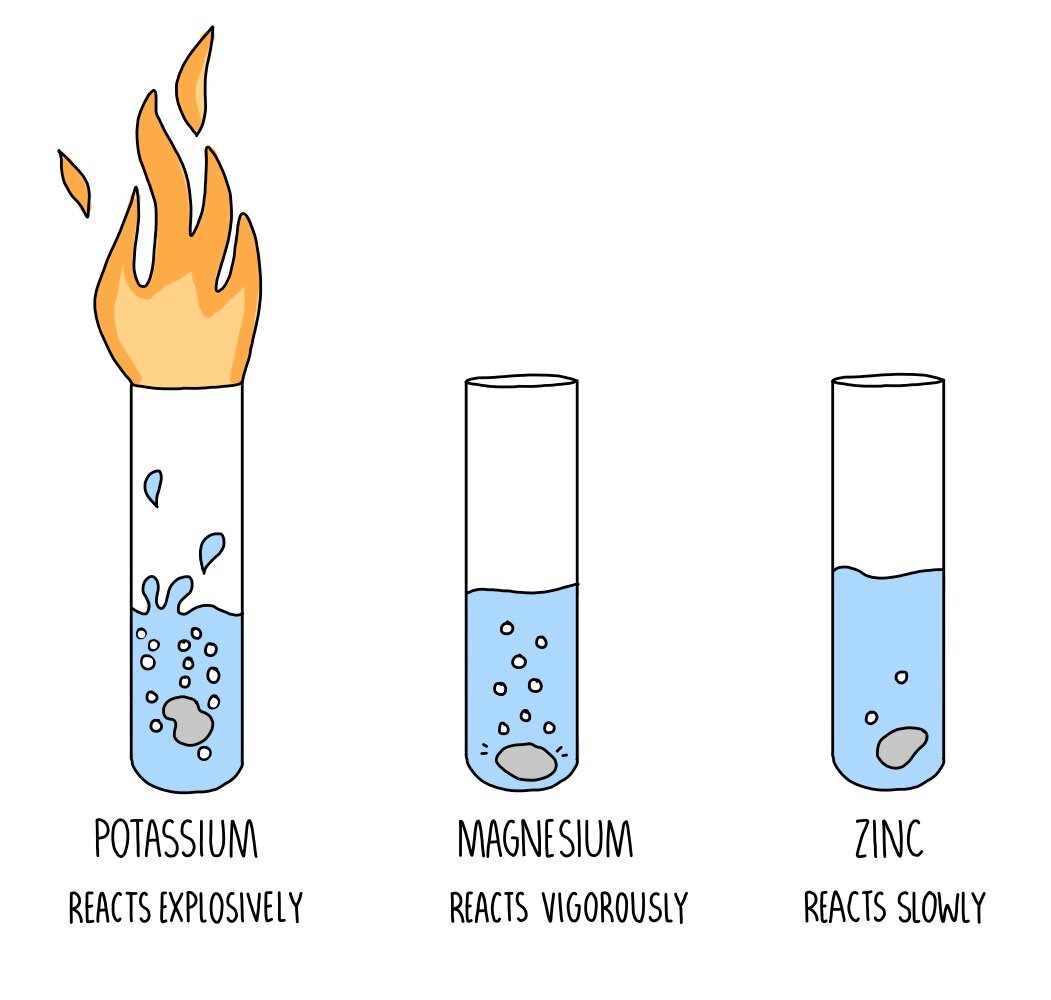
BBC Bitesize: Phytoextraction (phytomining) Introducing the reactions of metals and how they have been used to devise the reactivity series. BBC Bitesize: Extracting ironĮxtracting iron using a blast furnace, uses of iron and aluminium. The salts made in neutralisation reactions can be either soluble or insoluble. Four metals, W, X, Y and Z, were added separately to water and to dilute hydrochloric acid. The reactivity of a metal can be worked out by studying its reactions. Very unreactive metals, such as gold and platinum, are found in the Earth’s crust as pure metals. Metals can be arranged in order of their reactivity. The easier it is for a metal to form its positive ion, the more reactive the metal is. Iron and aluminium are extracted from their ores in various ways. You will need a copy of the periodic table 1. GCSE Edexcel Obtaining and using metals The reactivity series shows metals in order of reactivity. Reactivity Series When metals react with other substances, the metal atoms always form positive ions. AQA GCSE Chemistry 4: Chemical Changes Knowledge Organiser (Combined). Out of the elements in the reactivity series, the most reactive metal is potassium and the least reactive metal is copper. The reactivity series allows us to predict how metals will react. KS3 Reactivity Series Differentiated Homework Worksheets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
